How do You Test for Colorless Substances in Chromatography?
How Do You Test For Colorless Substances In Chromatography?
Thin Layer Chromatography/High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography is suitable for detection of organic and nonvolatile compounds.
There are many compounds which do not have chromophoric group therefore we can not see them with naked eyes. Sometimes these compounds have UV/fluorescence.
Such compounds can be detected by using suitable instrument like UV cabinet or CAMAG visualizer which can detect compounds in short UV i.e., 254nm, long UV i.e., 366nm and white light or if any compound is not UV active, a technique of derivatization can be used to make them visible.
UV detection, spectra and derivatization are powerful tools which helps in detection of colorless substances in High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography technique.
How colorless substances are analyzed by HPTLC?
HPTLC is a stepwise technique. One has to follow certain sequence while doing analysis.
- First step is application of sample on suitable stationary phase and using instrument like CAMAG Linomat 5 or ATS 4.
- Then the plate is developed in a suitable mobile phase and plate is observed in UV 254 and 366nm wavelength using instrument like CAMAG UV cabinet /Visualizer.
If compound is UV active (at 254nm) its presence can be checked by observing dark bands against green fluorescent background (Normal phase plates) and if it is fluorescent in nature fluorescent bands can be seen against dark background.
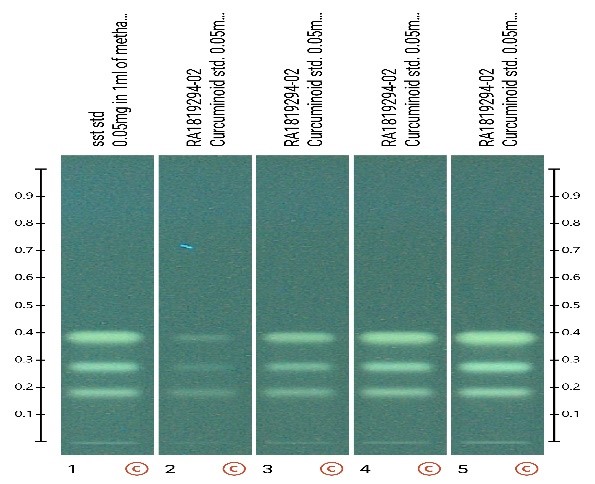
Image at 254nm: Image at 366nm:
CAMAG Scanner 4:

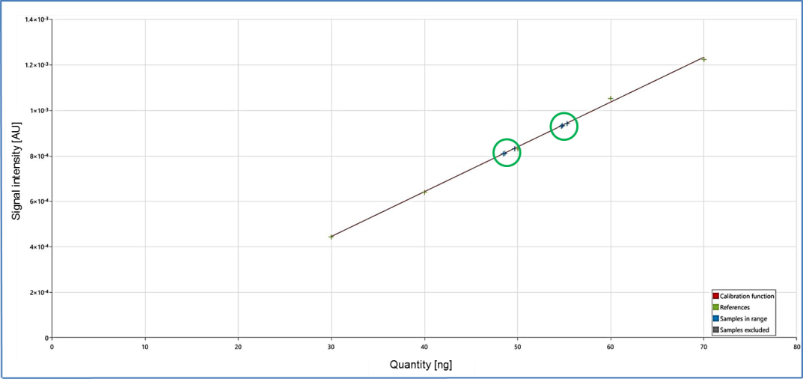
Some compounds show response in low UV range. If compound does not show any response in UV 254 nm that does not mean it is not present on your plate.
To ensure its presence in low UV light, the plate is scanned by using CAMAG scanner at different wavelengths or spectra can be taken from 190 to 400 nm and response can be recorded in low UV wavelength.
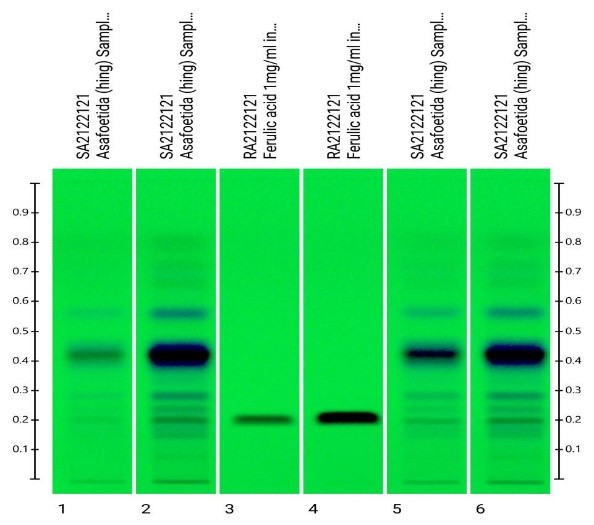
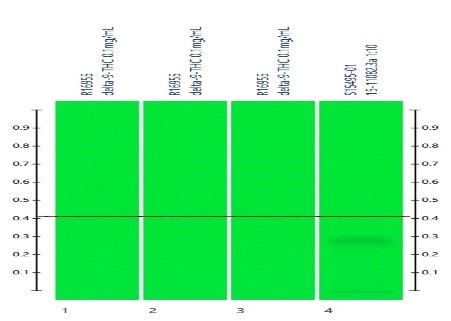
In the following example, analysis of cannabinoids was carried out. There are two major cannabinoids THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) and THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid). The band for THC cannot be seen on the plate (indicated its presence by horizontal line) because it shows response in low UV.
Whereas, the band for THCA can be seen on plate at Rf 0.4. When the plate was scanned in low UV light, the presence of THC was detected at 210 nm.
What is derivatization in chromatography?
CAMAG Derivatizer:

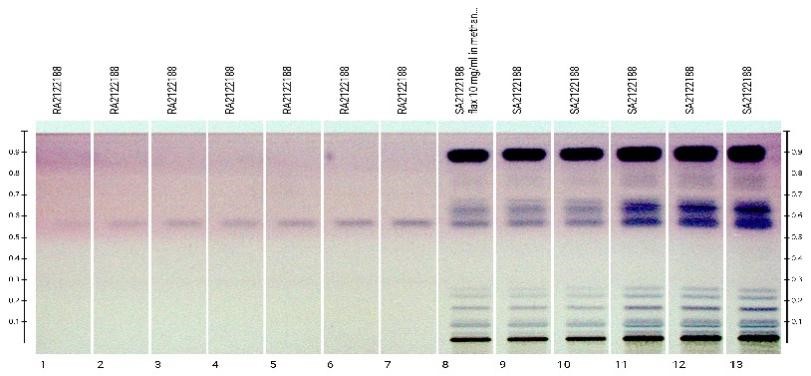
Derivatization is a technique in which a chromophoric group (colour adding group) is added to the compound in order to make it visible.
Derivatization is used to enable the detection of separated compounds that are colorless and cannot be visualized with UV radiation or fluorescence.
This is a chemical reaction which happens between the derivatizing reagent and the analyte. Many reactions require heat or thermo-chemical activation to complete the reaction. Popular ways of doing derivatization are dipping and spraying.
In following image, coloured bands can be seen after derivatization with anisaldehyde sulfuric acid:
Thus, HPTLC technique is a powerful, fast and cost-effective technique for detection of colorless substances.
By,
Dr. Manjusha Phanse
Project Leader
Anchrom Enterprises
Anchrom Enterprises Pvt. Ltd is one of the leaders in hptlc chromatography applications in india. Please contact us at lab@anchrom.in for HPTLC analysis of plant extracts, drugs, ingredients in cosmetics, and forensic science.

Comments
Post a Comment