Why HPTLC Is The Best Choice For Analysis Of Herbal Samples?
Why HPTLC Is The Best Choice For Analysis Of Herbal Samples?
HPTLC Method for Herbal Medicines
Herbal medicines are drugs which are originated from herbal ingredients. As herbal medicines are complex mixtures of many different types of components, it is very difficult and challenging task to analyze them.
Quality control, authenticity of the samples/products, safety concerns are difficult questions to answer affecting a huge market and covering many fields of herbal industry like Nutraceutical, Ayurvedic drugs, dietary supplements, Siddha drugs, Homeopathic drugs etc.
When herbal samples are in raw material form i.e., crude drug in the form of flowers, fruit, stem, root or leaves it is possible to identify the same by means of macroscopic and microscopic characteristics.
However, this type of study does not give much information about its chemical composition other than its authenticity or identity.
This composition can be affected by age, environmental factors such as mineral nutrition and stress, geographical origin and post harvesting handling and storage.
Why HPTLC is the best choice for analysis of herbal samples?
HPTLC is one of the best chromatographic techniques when it comes to analysis of herbal samples. HPTLC is now official technique in ‘United States Pharmacopoeia’ from 2018 for the analysis of materials of botanical origin. Analysis of materials of botanical origin means any herbal sample/formulation which is prepared from herbal ingredients.
This includes Ayurvedic, Homeopathic, Unani and Siddha medicines and Nutraceuticals and dietary supplements as well.
HPTLC offers many advantages like multiple samples can be applied and analyzed at the same time, about 15-20 samples can be applied on 20×10 cm size plate. Mobile phase requirement is only 20-30 ml that means per sample only 2-3 ml of mobile phase is required. Cheaper AR/GR grade solvents can be used which are half of the price of LC grade solvents.
Development time is less, roughly 20-30 minutes for many mobile phases. This significantly reduce the cost and time of analysis. Besides this, easy derivatization process and multiple choice and availability of various types of derivatizing reagent adds another dimension to HPTLC.
Many plant secondary metabolites or molecules which do not show any response in UV or fluorescence can be made visible and detected by this procedure.
And most important advantage is, as herbal sample are made up of many complex components, they are very difficult and challenging to analyze by other techniques as lot of precautions has to be taken before analyzing them.
In HPTLC, as every time new plate is used for analysis there are no chances of contamination or carryover. Any unknown herbal samples can also be put directly on the system for analysis.
HPTLC has many applications in herbal analysis like:
- HPTLC Fingerprinting studies for identification of herbal samples/formulations w.r.t botanical reference material and confounded material
- Identification, quantification and validation studies of phylomarkers
- Class of compound studies for identification of secondary metabolites
- HPTLC bioassays or bioautography studies like antioxidant activity, α-glucosidase assays for antidiabetic activity, Ache assay etc.
- Identification of synthetic adulterants/API in herbal samples/formulation by MS for detection of synthetic adulterants
- Stability studies
Let us take one example to understand how HPTLC is useful for the analysis of herbal sample:
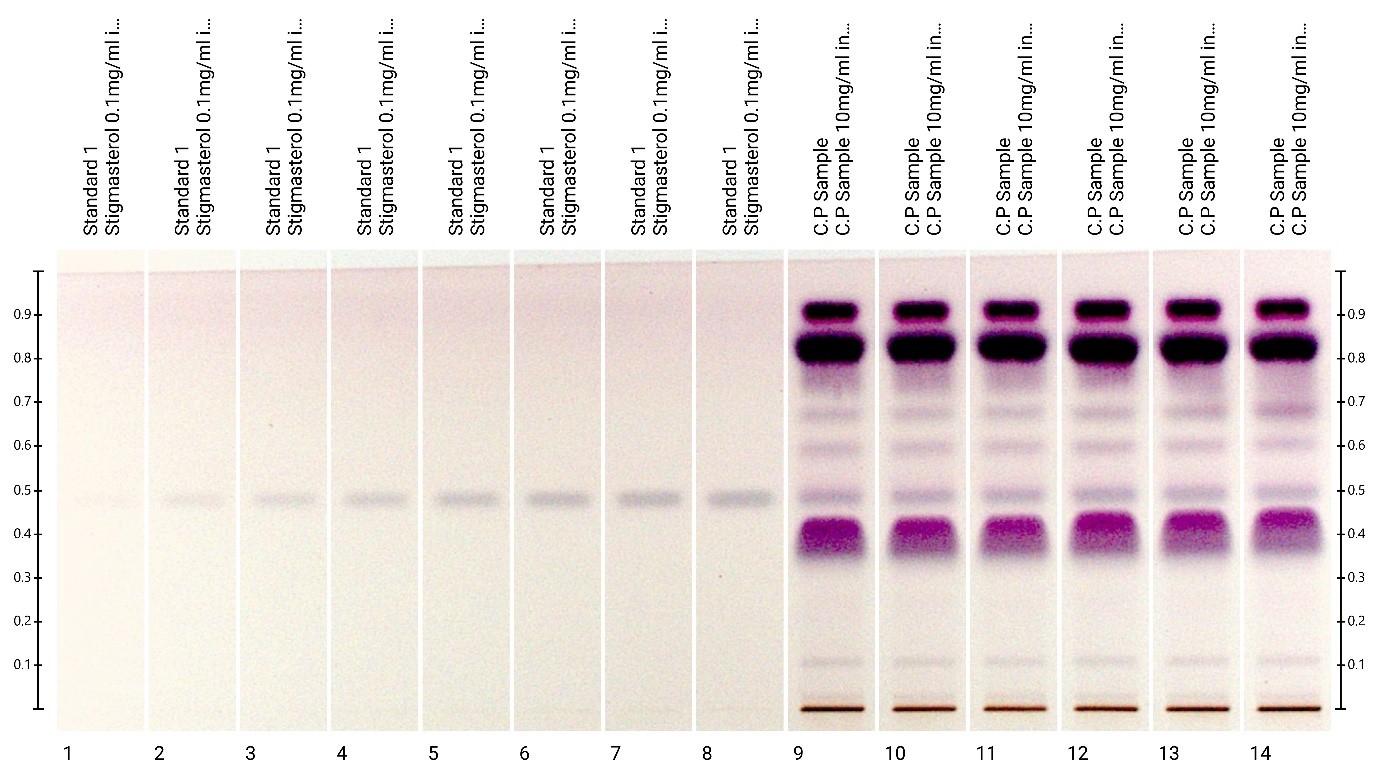
Method development and quantification of stigmasterol in Celastrus paniculatus:
C.paniculatus (known as Jyotishmati in Sanskrit and Malkangni in Hindi), is an important medicinal plant of India. Oil obtained from the seeds of this plant is a source of herbal medicine, which is used in the treatment of gout, leprosy, skin diseases, fever, rheumatism, beriberi, sores and neurological disorders
Stigmastrol- a plant sterol-is one of the marker found in C. paniculatus. HPTLC method was developed for quantification and validation of stigmasterol in C. paniculatus sample. Plate was derivatized with anisaldehyde sulfuric acid for detection of stigmasterol. Stigmasterol is detected at 0.24% in C. paniculatus sample.

b. Fruits of C. paniculatus
c. Dried seeds of C. paniculatus
Anchrom Enterprises Pvt. Ltd is one of the leaders in HPTLC for Herbal Medicine. Please contact us at lab@anchrom.in for HPTLC analysis of plant extracts, drugs, ingredients in cosmetics, and forensic science.

Comments
Post a Comment